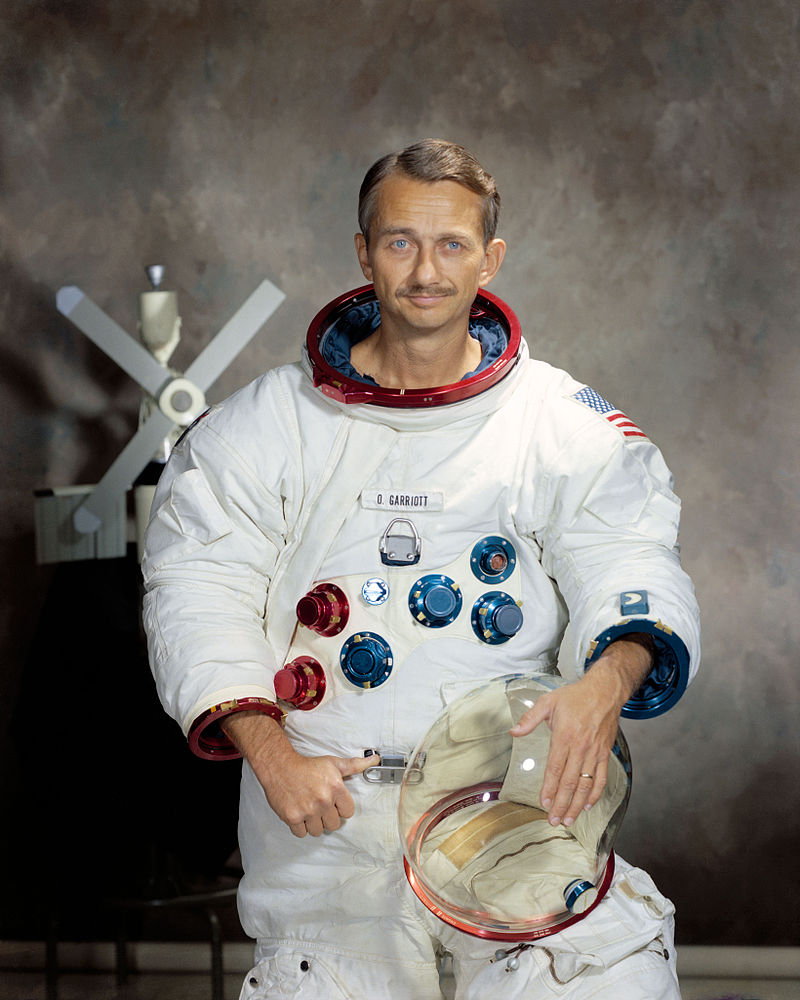
It is with great sadness that the ARISS team recognizes the passing of our great friend and colleague Astronaut Owen Garriott, W5LFL (SK). Owen Garriott died at his home in Huntsville, Alabama on April 15, 2019.
A passionate amateur radio operator and ionospheric physics researcher, Owen inspired the amateur radio community to reach for the stars. His multi-decade vision to bring amateur radio with him as part of his journey in space was realized in 1983 on the STS-9 Space Shuttle Columbia mission, where hams the world over for the first time heard a fellow ham call CQ from space. As the first to operate ham radio in space, Owen blazed a trail that has enabled countless people from around the world to experience what it is like to journey into space and explore our universe. As a result, he inspired the international amateur radio community to extend his modest ham station on STS-9 into an international human spaceflight ham radio program that has spanned the Space Shuttle, Mir Space Station, and International Space Station.
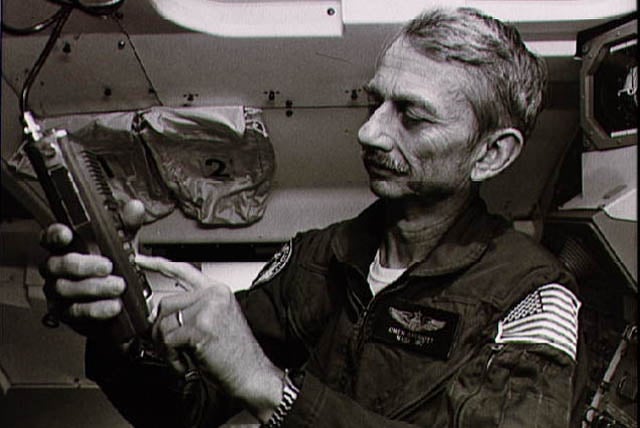

A member of the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame, Owen Garriott was a pioneer and innovator in all his endeavors…including amateur radio. Selected as a NASA scientist-astronaut in 1965, Garriott was the science-pilot for Skylab 3, the second crewed Skylab mission. Skylab was the first U.S. space station, housing 3 different crew expeditions from May 1973-February 1974. Owen spent approximately 60 days on Skylab, doing solar physics research, human physiological research and conducting 3 spacewalks to repair Skylab and extend its research capabilities.
Owen’s next flight into space, as part of an international crew on the STS-9 Space Shuttle Columbia mission, cemented amateur radio’s future as part of the human spaceflight experience. STS-9 was launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida on November 28, 1983. Onboard Columbia was an internationally developed space laboratory, Spacelab-1, which pioneered international spaceflight research with over 70 separate experiments—a precursor to the research currently being accomplished on the International Space Station (ISS). Onboard also was a Motorola 2-meter handheld radio with a window mounted antenna to facilitate ham radio contacts between W5LFL and hams on the ground. On December 1, the third day of his mission, Owen donned his headset and made history by communicating with Lance Collister, WA1JXN, in Frenchtown, Montana. In W5LFL’s own words, here is an excerpt of his first contact: “W5LFL in Columbia is calling CQ and standing by. Go ahead. Hello WA1JXN, WA1 Juliet X‐ray November, this is W5LFL. I picked up your signals fairly weakly. I think our attitude is not really the best as yet, but you’re our first contact from orbit. WA1 Juliet X‐ray November, how do you read? Over.”

Owen’s ham contacts on STS-9 were trailblazing for many reasons. They represented the first ham radio contact from a human in space to someone on Earth. They allowed the general public to directly listen and communicate with an on-orbit crew where, prior to this, only NASA mission control personnel or heads of State (U.S. Presidents, etc.) could talk to astronauts from space. And the mission also demonstrated that a group of volunteers could successfully build a ham radio station for a human spaceflight vehicle and get it formally approved by a space agency.
Owen spent decades attempting to carry out ham radio on one of his missions, employing gentle assertiveness and steadfast patience to realize his dream. In 1965, when NASA was considering Owen for a planned lunar flight on Apollo 18, 19 or 20, Project MOONRAY was proposed by the Project OSCAR team. Project MOONRAY would support amateur radio operations from the surface of the moon. This initiative was scuttled when Apollo lunar expeditions ended at Apollo 17. Prior to his flight on Skylab, AMSAT submitted a proposal to NASA called SKYLARC (Skylab Amateur Radio Communications). Unfortunately, this proposal was turned down. But, as they say, the 3rd time was a charm on STS-9 and ham radio is now a human spaceflight reality. Also, it should be noted that an AMSAT/ARISS International team is pursuing Owen’s plans to fly ham radio to the moon via several lunar proposal initiatives, including the Lunar Gateway.
Owen inspired legions of amateur radio operators, world-wide, to support human spaceflight amateur radio endeavors and for countless individuals to become ham radio operators. This includes his son, Richard, W5KWQ, who together with Owen became the first multi-generational American ham radio operators to communicate from space.
On behalf of the ARISS International Team, we would like to extend our sincere condolences to the Garriott family, including Owen’s son Richard, W5KWQ and Owen’s wife Eve. As Owen has inspired the amateur radio community to reach for the stars may we wish Owen Garriott Godspeed and a wonderful journey amongst the stars.
Ad Astra!
73, Frank Bauer, KA3HDO
ARISS International Chair
AMSAT V.P. for Human Spaceflight Programs