In this edition:
* ARISS SSTV Event Starts July 14
* Registration Opens for 43rd Annual AMSAT Space Symposium & Annual General Meeting
* ARISS Call for Proposals for School Contacts Began July 9
* 2025 President’s Club Members Hit $65,000 YTD
* SDR Provides New Capabilities For Next AMSAT CubeSats
* Changes to AMSAT-NA TLE Distribution
* ARISS News
* AMSAT Ambassador Activities
* Satellite Shorts From All Over
The AMSAT(R) News Service bulletins are a free, weekly news and information service of AMSAT, the Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation. ANS publishes news related to Amateur Radio in Space including reports on the activities of a worldwide group of Amateur Radio operators who share an active interest in designing, building, launching and communicating through analog and digital Amateur Radio satellites.
The news feed on http://www.amsat.org publishes news of Amateur Radio in Space as soon as our volunteers can post it.
Please send any amateur satellite news or reports to: ans-editor [at] amsat.org
Sign up for free e-mail delivery of the AMSAT News Service Bulletins via the ANS List; to join this list see: https://mailman.amsat.org/postorius/lists/ans.amsat.org/
ARISS SSTV Event Starts July 14
Amateur Radio on the International Space Station (ARISS) has announced Slow Scan Television (SSTV) Series 28 to run from July 14-20, 2025.
The theme will be the Apollo Soyuz mission and STS-51F which pioneered SSTV on Shuttles.

This series of 12 images will be transmitted from the ISS on 145.800 MHz using PD120 encoding. Software needed to decode the pictures is free and is available for PC’s, Mac’s, Android smartphones, and iPhones. Search “SSTV software” on Google and your phone’s app store for a variety of options.
Transmissions from the ISS are powerful enough so images can be received with a handheld radio and its stock rubber duck antenna, albeit quite noisy. The addition of a simple homemade 3-element beam to the handheld can produce in pixel perfect images. Persons who are not familiar with SSTV operations can visit https://amsat-uk.org/beginners/iss-sstv/.
You are invited to upload decoded images in the ARISS gallery, area “ARISS Series 28 Apollo Soyuz and STS-51F” at: https://ariss-usa.org/ARISS_SSTV/. Once you’ve submitted your pictures, just click on the dedicated button to apply for the official ARISS SSTV award.
Transmissions will begin on Monday, July 14 at 09:15 UTC (05:15 AM Eastern time). Transmissions will cease on Sunday, July 20 at 18:00 UTC (2:00 PM Eastern time).
[ANS thanks ARISS and AMSAT-UK for the above information.]
Your 2025 AMSAT President’s Club Coin Is Waiting!
Celebrating the 40th Anniversary of Amateur Radio on Human Spaceflight
Help Support GOLF and Fox-Plus.

Join the AMSAT President’s Club today and help
Keep Amateur Radio in Space!
https://www.amsat.org/join-the-amsat-presidents-club/
Registration Opens for 43rd Annual AMSAT Space Symposium & Annual General Meeting
Registration is now open for the 43rd Annual Space Symposium & Annual General Meeting to be held October 16-19 in Phoenix, Arizona. You can catch the ground-breaking presentations, enjoy good food and exchange ideas with your friends, old and new, in the world of amateur satellites. The overall schedule is:
Thursday, October 16th
0900 – 1700 Board of Directors Meeting
Friday, October 17th
0900 – 1200 Board of Directors Meeting
1300 – 1700 Symposium Presentations
1800 – 2100 Reception & Auction
Saturday, October 18th
0900 – 1200 Symposium Presentations
1300 – 1500 Symposium Presentations
1500 – 1700 Annual General Meeting
1800 – 1900 Reception
1900 – 2100 Banquet
Sunday, October 19th
0800 – 1000 Members Breakfast
Register Now and Save!
Good News! No price increase over previous years’ Symposiums if you register now. Register for the Symposium before September 15 and save $20.
Early Bird Registration
* Symposium Registration is $75
* Banquet registration is $55
Regular Registration
* Symposium Registration is $85
* Banquet registration is $65
Save $20 and Register Today at:
https://launch.amsat.org/events.

Reserve Your Hotel Room Now!
* The Holiday Inn & Suites Phoenix Airport North is located minutes away from Phoenix Sky Harbor airport and features:
* Free airport shuttle and free parking
* Resort-style facility with beautiful courtyard
* Outdoor pool
* Brew pub
* Fitness center
* Free breakfast
* Fully updated rooms
* All rooms are two-room suites with choice of 2 Queen beds or 1 King Bed
* Affordable rates of only $129 plus tax.
Rooms at these Discounted Rates are Limited.
You must make your reservation directly with the hotel to enjoy this special rate.
Call Reservations at 877-424-2449.
Use Group Code: P7C and Group Name: AMSAT.
[ANS thanks AMSAT for the above information.]
ARISS Call for Proposals for School Contacts Began July 9
The Amateur Radio on the International Space Station (ARISS) Program is seeking formal and informal education institutions and organizations, individually or working together, to host an Amateur Radio contact with a crew member on board the ISS. ARISS anticipates that the contact would be held between January 1, 2026 and June 30, 2026. Crew scheduling and ISS orbits will determine the exact contact dates. To maximize these radio contact opportunities, ARISS is looking for organizations that will draw large numbers of participants and integrate the contact into a well-developed education plan.
 Crew members aboard the International Space Station will participate in scheduled Amateur Radio contacts. These radio contacts are approximately 10 minutes in length and allow students to interact with the astronauts through a question-and-answer session.
Crew members aboard the International Space Station will participate in scheduled Amateur Radio contacts. These radio contacts are approximately 10 minutes in length and allow students to interact with the astronauts through a question-and-answer session.
The deadline to submit a proposal is August 29th, 2025. Proposal information and more details such as expectations, proposal guidelines and the proposal form can be found at www.ariss.org.
An ARISS Introductory Webinar session will be held on July 30th at 7 PM ET. The Zoom link to sign up is: https://us06web.zoom.us/meeting/register/E0qy2calSqudqufl09PL8A
Questions should be directed to [email protected].
[ANS thanks Dave Jordan, AA4KN, ARISS PR for the above information]
Need new satellite antennas?
Purchase M2 LEO-Packs from the AMSAT Store.
When you purchase through AMSAT, a portion of the proceeds goes towards
Keeping Amateur Radio in Space.
https://amsat.org/product-category/hardware/
2025 President’s Club Members Hit $65,000 YTD
AMSAT President, Robert Bankston, KE4AL thanks 2025 President’s Club members who have so far this year donated an amazing $65,544. It is because of these especially generous donors that AMSAT has the resources to Help Keep Amateur Radio in Space. With the Fox-Plus and GOLF-TEE satellites nearing flight readiness, AMSAT especially appreciates these contributions to help purchase flight-proven parts, specialized software licenses, test fees, shipping and travel costs. It just couldn’t be done without your support.
 Contributors to date include:
Contributors to date include:
Titanium ($4,800+)
Barry Baines, WD4ASW
Alan Biddle, WA4SCA
William Brown, K9LF
Bruce Paige, KK5DO
Walter Wittenberg, K0CEH
Platinum ($2,400+)
Ray Crafton, KN2K
Douglas Tabor, N6UA
Gold ($1,200+)
Mark Hammond, N8MH
Frank Karnauskas, N1UW
John Kludt, K7SYS
Glenn Miller, AA5PK
Mary Lou Monteiro
Silver ($600+)
Joseph, Lynch,N6CL
Jason Schwarz, N4JJS
Scott Shaheen, WB8OOJ
Bronze ($300+)
Keith Baker, KB1SF
Edward Krome, K9EK
Donald Pettigrew, K9ECT
Dave Taylor, W8AAS
Core ($120+)
Mitch Ahrenstorff, AD0HJ
Alan Boggs, K7IIV
Richard Dittmer, KB7SAT
David Hartrum, WA3YDZ
Doug Papay, K8DP
William Pesci, N4WLP
Tim Pierce, N9PN
Martin Shinko, KB3AEV
Paul Stoetzer, N8HM
Wayne Wagner, AG1A
Jim Wilmerding, W2NNU
There are still nearly six months left to become a member of the 2025 President’s Club. Join today at https://www.amsat.org/product-category/amsat-presidents-club-donations/.
[ANS thanks ANS for the above information.]
SDR Provides New Capabilities For Next AMSAT CubeSats
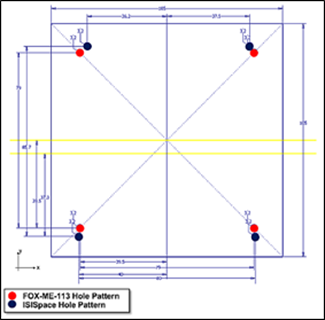
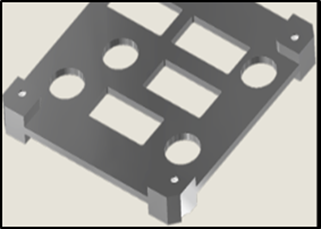
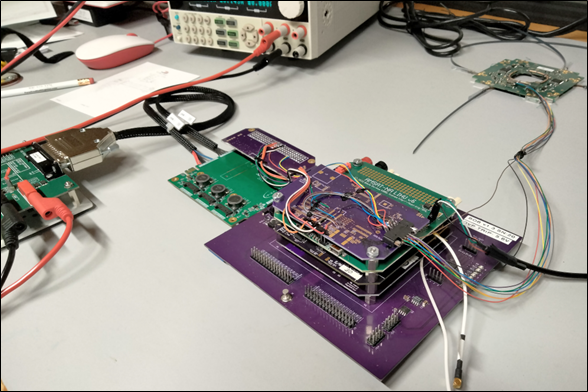
Rich Gopstein, KD2CQ and Bill Schell, W2WZ highlighted new systems aboard AMSAT’s new GOLF CubeSat at Hamvention 2025. Rich detailed the software defined radio (SDR) module while Bill explained how the SDR communicates with other systems on the upcoming GOLF satellites.
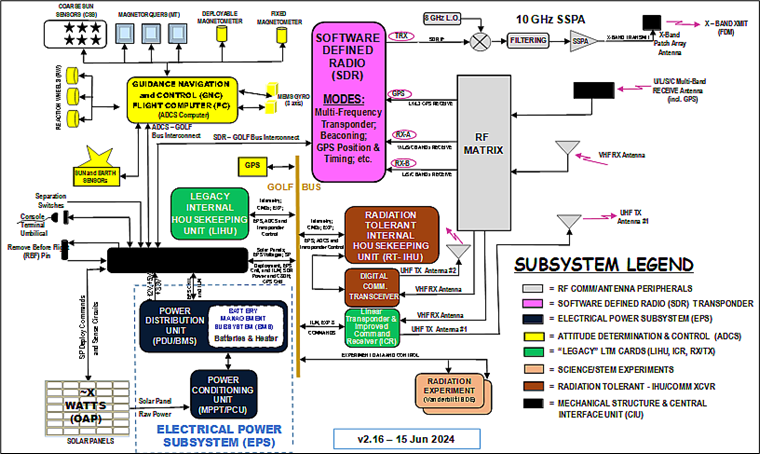 Rich explained, “The diagram above is a block diagram of the GOLF-TEE 3U CubeSat. The purple rectangle located in the middle of the diagram represents a (SDR). The Fox series of satellites before had transponders. Some were FM transponders. They acted like a repeater up in the sky. A single FM channel up with a single FM channel down. Other Fox satellites had linear transponders with wide bandwidths for several SSB or CW signals. Whatever you sent up to the satellite, either on 2 meters or 440, would come down on the other band.
Rich explained, “The diagram above is a block diagram of the GOLF-TEE 3U CubeSat. The purple rectangle located in the middle of the diagram represents a (SDR). The Fox series of satellites before had transponders. Some were FM transponders. They acted like a repeater up in the sky. A single FM channel up with a single FM channel down. Other Fox satellites had linear transponders with wide bandwidths for several SSB or CW signals. Whatever you sent up to the satellite, either on 2 meters or 440, would come down on the other band.
“You could communicate with people that way, operate either FM or linear transponder, but that’s all you could do with a transponder. On the other hand, the SDR allows us to do much more interesting things. Instead of the radio being permanently built into the hardware like it was in the Fox series, with an SDR it’s all done in software. We don’t have to change the hardware to implement different modes like SSTV or any of the voice, data or image operations we want to try. With an SDR we can do it in software. It’s much easier much quicker to do.
“The SDR communicates with the RF matrix, represented by the light gray rectangle to the right of the SDR. The SDR communicates and is controlled by other circuits in the satellite through the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus shown to the left of the SDR. That control bus is used to activate and deactivate the radio system as well as command it to perform a variety of operations.”
Specifically the SDR for the first GOLF satellites is the Ettus Research™ E310 Universal Software Radio Peripheral (USRP™). Rich explained, “The Ettus 310 SDR has two receive and two transmit antenna connections, which gives us a lot of flexibility in terms of what we want to do. For example, we can create cross-band transponders with it. We will use the radio at 5 GHz and 10 GHz, but it can’t do 10 GHz natively. We need to implement some RF hardware externally to increase the original frequency range to 10 GHz.
“The Ettus runs on a Linux operating system so we will use GNU Radio software to program radio functions. So, if we want to have the radio operate as a transponder, for Morse code, telemetry, SSTV, or whatever, we can do it can through programming.”
It is a free and open-source software development toolkit that provides signal processing blocks to implement software radios. Gopstein remarked, “GNU Radio makes programming easier! The talent and skills of AMSAT engineers are a precious resource. The GNU building block approach saves time while elevating consistency, quality and production rates for the benefit of all AMSAT satellite end users.
“We’re using GNU Radio to support radio necessities such as the spacecraft transponder, telemetry and other modes of data transmission for the GOLF satellites. These are just a portion of the functions we’re capable of using.
“Because the Ettus E310 SDR connects to the RF matrix, various antennas on the satellite can be connected to the SDR. As I said before, the output from the SDR will have a 10 GHz frequency converter and we will also have a solid-state power amplifier. That combination will increase frequency and output power for transmission at 10 GHz then sending the RF to an X band patch antenna.”
“One element of RF operation that we’re definitely going to try with the SDR is a 1 megabits per second (Mbps) data transmission. Another exciting experiment with the SDR could be ‘five-and-dime’ 5GHz/10GHz microwave radio transponder. On future missions, we expect to use the SDR to try all sorts of other functions with the SDR, yet to be determined,” Rich concluded.
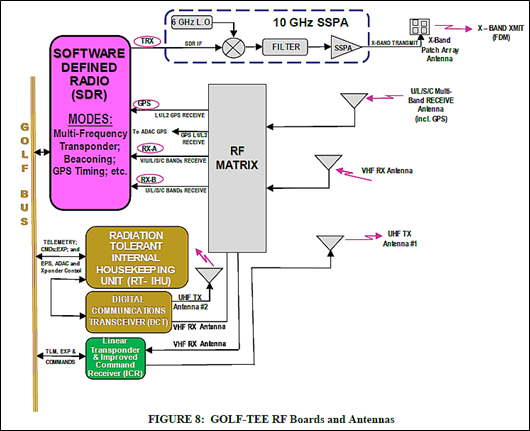 Next, Bill Schell, W2WZ went on to say, “This block diagram is a detailed look at part of the original diagram. It shows the Ettus E310 SDR connected to the main control processor of GOLF-TEE, the RT-IHU (Radiation Tolerant Internal Housekeeping Unit). The two are connected over the CAN bus, over which messages flow in each direction.”
Next, Bill Schell, W2WZ went on to say, “This block diagram is a detailed look at part of the original diagram. It shows the Ettus E310 SDR connected to the main control processor of GOLF-TEE, the RT-IHU (Radiation Tolerant Internal Housekeeping Unit). The two are connected over the CAN bus, over which messages flow in each direction.”
“The RT-IHU control software communicates with a python application running on the E310 called ‘SDR Server’. This application receives request messages from the RT-IHU to execute various SDR related actions. It also sends E-310 related status and telemetry information back to the RT-IHU”, Bill added.
According to Bill, “One of the most important actions the RT-IHU requests through SDR server is to start and stop GNU radio flows on the E-310. These flows are the software that implement the radio functions of the SDR. A flow might implement a transponder, the transmission of a periodic morse code ID, or the transmission of a data file to a ground station. Flows are created from building blocks in the GNU radio user interface. Common types of blocks include signal sources, filters, modulators, demodulators, FFT’s, math operations, etc. Blocks are combined to implement a flow which accomplishes a particular radio or signal processing task.”
“Other actions the SDR server performs are the sending of IMU and temperature data to the RT-IHU, receiving a file for later transmission (by a flow), shutdown, and other housekeeping functions”, Bill concluded.
[ANS thanks AMSAT for the above information]
Want to fly the colors on your own grid expedition?
Get your AMSAT car flag and other neat stuff from our Zazzle store!
25% of the purchase price of each product goes towards
Keeping Amateur Radio in Space
https://www.zazzle.com/amsat_gear
Changes to AMSAT-NA TLE Distribution for July 11
Two Line Elements or TLEs, often referred to as Keplerian elements or keps in the amateur community, are the inputs to the SGP4 standard mathematical model of spacecraft orbits used by most amateur tracking programs. Weekly updates are completely adequate for most amateur satellites. TLE bulletin files are updated daily in the first hour of the UTC day. New bulletin files will be posted immediately after reliable elements become available for new amateur satellites. More information may be found at https://www.amsat.org/keplerian-elements-resources/.
This week there are no additions or deletions to the AMSAT TLE distributions.
[ANS thanks Joe Fitzgerald, KM1P, AMSAT Orbital Elements Manager for the above information]
ARISS NEWS
Amateurs and others around the world may listen in on contacts between amateurs operating in schools and allowing students to interact with astronauts and cosmonauts aboard the International Space Station. The downlink frequency on which to listen is 145.800 MHz worldwide.
 There are no scheduled contacts at this time.
There are no scheduled contacts at this time.
The crossband repeater continues to be active (145.990 MHz up {PL 67} & 437.800 MHz down). If any crewmember is so inclined, all they have to do is pick up the microphone, raise the volume up, and talk on the crossband repeater. So give a listen, you just never know.
The packet system is also active (145.825 MHz up & down).
As always, if there is an EVA, a docking, or an undocking; the ARISS radios are turned off as part of the safety protocol.
Note, all times are approximate. It is recommended that you do your own orbital prediction or start listening about 10 minutes before the listed time.
The latest information on the operation mode can be found at https://www.ariss.org/current-status-of-iss-stations.html
The latest list of frequencies in use can be found at https://www.ariss.org/contact-the-iss.html
[ANS thanks Charlie Sufana, AJ9N, one of the ARISS operation team mentors for the above information]
AMSAT Ambassador Activities
AMSAT Ambassadors provide presentations, demonstrate communicating through amateur satellites, and host information tables at club meetings, hamfests, conventions, maker faires, and other events.
 August 21-24, 2025
August 21-24, 2025
Northeast HamXposition (HamX) & New England ARRL Convention
Best Western Royal Plaza & Trade Center
181 Boston Post Road W
Marlborough, MA 01752
http://www.HamX.org
W1EME, WD4ASW, WB1FJ
September 6, 2025
Greater Louisville Hamfest
Paroquet Springs Conference Centre
395 Paroquet Springs Drive
Shepherdsville, KY 40165
W4FCL
October 16, 17, 18, 19, 2025
AMSAT Board of Directors Meeting and 43rd Annual AMSAT Space Symposium & Annual General Meeting
Holiday Inn & Suites Phoenix Airport North
1515 North 44th Street
Phoenix, Arizona 85008
Details at https://www.amsat.org/2025-symposium/
[ANS thanks Bo Lowrey, W4FCL, Director – AMSAT Ambassador Program, for the above information]
Satellite Shorts From All Over
+ AMSAT SA has announced that its 2025 Space Symposium will be held on August 2, 2025 and has issued the first call for papers. The theme of the symposium is “Embracing 68 years of space science innovation in Amateur Radio”. Papers are invited covering all aspects of space science and communication impacting and enhancing the Amateur Radio experience, from the technical to operational aspects. Presentations are typically 30 minutes a with a 10-minute Q&A. Send proposals in MS Word to [email protected] by July 9, 2025. The symposium will be held online on Webex. Register at https://forms.gle/vY9oGJekxzcg5j4c9.
+ ESA, Telesat and the Science and Technology Facilities Council’s (STFC) RAL Space have reported a groundbreaking milestone in telecommunications technology, successfully establishing a Q-Band (38-39 GHz) link over LEO, between the RAL Space Chilbolton Observatory and the Telesat LEO 3 demonstration satellite. A Q-Band receiver was mounted on Chilbolton Observatory’s large 25m dish. The team at the observatory used this radar tracking capability to monitor the state of the satellite and its orbit during each pass. The team established a stable link with a collocated Ka-Band uplink antenna to the Telesat LEO 3 satellite. The Telesat LEO 3 satellite also provided frequency up-conversion to Q-Band, amplification and retransmission to ground. The Telesat satellite station transmitted a DVBs signal. Full story at https://tinyurl.com/ANS-194-Q-Band.
Join AMSAT today at https://launch.amsat.org/
In addition to regular membership, AMSAT offers membership to:
* Societies (a recognized group, clubs or organization).
* Primary and secondary school students are eligible for membership at one-half the standard yearly rate.
* Post-secondary school students enrolled in at least half time status shall be eligible for the student rate for a maximum of 6 post-secondary years in this status.
* Memberships are available for annual and lifetime terms.
Contact info [at] amsat.org for additional membership information.
73 and remember to help Keep Amateur Radio in Space!
This week’s ANS Editor, Frank Karnauskas, N1UW
f.karnauskas [at] amsat [dot] org
ANS is a service of AMSAT, the Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation, 712 H Street NE, Suite 1653, Washington, DC 20002.
AMSAT is a registered trademark of the Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation.


 Purchase M2 LEO-Packs from the AMSAT Store.
Purchase M2 LEO-Packs from the AMSAT Store.






 (Photo Credit: JUPITER)
(Photo Credit: JUPITER) Starlink satellites are featured in this file photo (Dec. 2024) taken by NASA astronaut Don Pettit from the International Space Station (ISS). (Photo credit: Don Pettit/NASA via SWNS and Talker.com)
Starlink satellites are featured in this file photo (Dec. 2024) taken by NASA astronaut Don Pettit from the International Space Station (ISS). (Photo credit: Don Pettit/NASA via SWNS and Talker.com) 2025 ARRL Field Day logo (Credit: ARRL)
2025 ARRL Field Day logo (Credit: ARRL)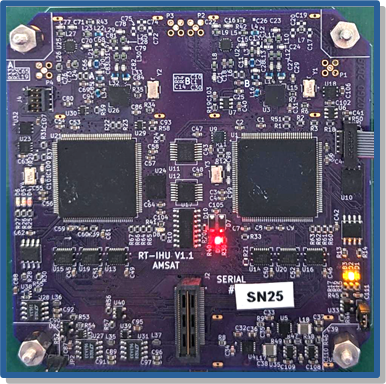
 Purchase M2 LEO-Packs from the AMSAT Store.
Purchase M2 LEO-Packs from the AMSAT Store.